Search:
DSCF with missing actual-values for the failure rate (FIT)
Explanation:
A search will be made for base failures
a) for which no FIT value for the failure rate has been assigned and
b) which are linked to failures that are anchored at functions with safety goals (see properties dialog) and have
a safety level (SIL/ASIL) not equal to QM
Note:
- A DSCF (Dangerous Safety-Critical Failure) is a failure which has a safety level (SIL/ASIL) not equal to QM (Quality Management). The function at which the DSCF is anchored is automatically defined as a safety goal (see Properties dialog „Functional Safety“).
- Base failures (BF) are failures which have effects but no causes.
Example:
Abbreviations
- ASIL = Automotive safety integrity level
- BF = Base failure of a base function
- BFn = Base function of a base structure element
- BSE = Base structure element
- Cl Prc = Classification for process characteristic
- Cl Prd = Classification for product characteristic
- Cl Req = Classification for requirement
- CM = Control method
- DA = Detection action
- DC = Diagnostic coverage
- DSCF = Dangerous safety critical failure
- Er Det = Error detection
- Er Resp = Error response
- F = Failure
- FIT = Failure in time
- Fn = Function
- FSM = Functional safety management
- IE = Inspection equipment
- LF = Latent fault
- LFM = Latent fault metric
- OC = Operating condition
- PA = Preventive action
- PE = Process element
- PFH = Probability of failure per Hour
- PMHF = Probabilistic metric for random hardware failures
- PrcC = Process characteristic
- PrdC = Product characteristic
- QM = Quality method
- QR = Quality rule
- Req = Requirement
- RMR = Risk Matrix Ranking
- RP = Reaction plan
- SE = Structure element
- SE ErDet = Structure element for error detections
- SE ErResp = Structure element for error responses
- SFF = Safe failure fraction
- SG = Safety Goal
- SIL = Safety integrity level
- SM = Organisational-SE for “safety mechanisms”
- SPF = Single point fault
- SPFM = Single point fault metric
- TF = Top failure of a top function
- TFn = Top function at root element
- TS = Test sample
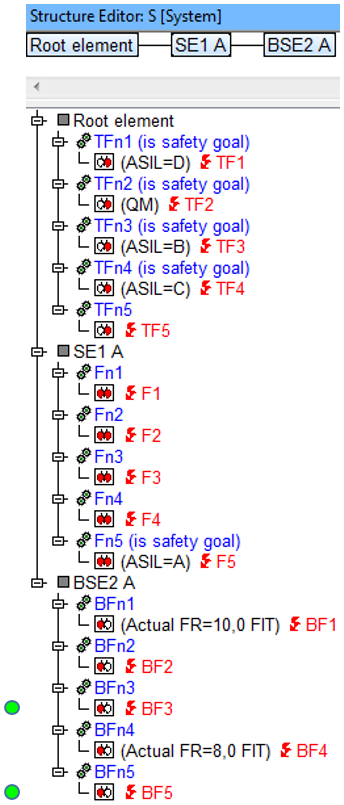
- The above structure contains three system elements, each with five functions which in turn have a single failure. The functions that contain safety goals have this info in brackets in the function name. The IQ-Software automatically identifies a function as a safety goal if at least one failure anchored below this function has a SIL/ASIL value unequal to QM.
- The purpose of this Quality Rule is to detect those basic failures (BF) that do not have a FIT value for the failure rate but are linked to failures which have at least one QM that differs from the safety level. Fürthermore, these failures must have safety goals assigned.
- Through this visual analysis of the failure net links from the viewpoint of the base failure and with certain display options active in the failure net (here: “Function” and “Functional Safety parameters”), it is possible to see which hits this Quality Rule will deliver.
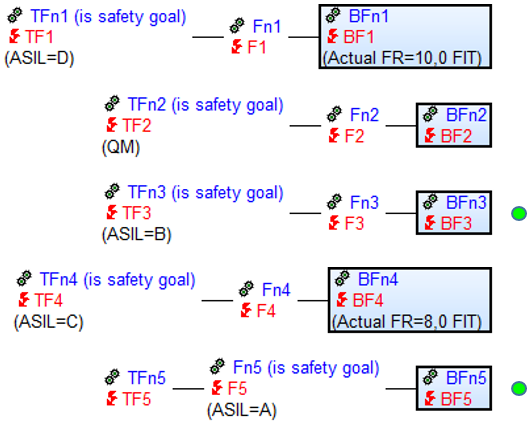
Search result: ![]()
From the five base failures, two meet all the requirements to be identified as a hit with this Quality Rule.
BF1 and BF4 are not considered in this search, as both have FIT values assigned.
BF2 is also not a hit, even though it doesn’t have a FIT value. This is because BF2 is linked to a failure anchored to a function with a safety goal, whose safety level is to low.
BF3 and BF5 meet all the conditions to be hits. They are both linked to failures which have at least one safety level that differs from the QM and are anchored at functions with safety goals. Furthermore, both have base failures with no FIT value.