Search:
Base failures which have effects that have safety goals and not secured with an error response
Explanation:
A search will be performed for base failures, which have a safety-critical failure as its effect and this effect has no error response assigned. A safety-critical failure is when the (A)SIL value is greater than the QM. Base failures, which it was not agreed that an error response is not necessary will not be considered. This specification is made in the Object Inspector under the “Functional Safety” tab.
Note:
- Base failures (BF) are failures which have effects but no causes.
- Safety mechanisms are error detections and error responses
- A DSCF (Dangerous Safety-Critical Failure) is a failure which has a safety level (SIL/ASIL) not equal to QM (Quality Management).
Abbreviations
- ASIL = Automotive safety integrity level
- BF = Base failure of a base function
- BFn = Base function of a base structure element
- BSE = Base structure element
- Cl Prc = Classification for process characteristic
- Cl Prd = Classification for product characteristic
- Cl Req = Classification for requirement
- CM = Control method
- DA = Detection action
- DC = Diagnostic coverage
- DSCF = Dangerous safety critical failure
- Er Det = Error detection
- Er Resp = Error response
- F = Failure
- FIT = Failure in time
- Fn = Function
- FSM = Functional safety management
- IE = Inspection equipment
- LF = Latent fault
- LFM = Latent fault metric
- OC = Operating condition
- PA = Preventive action
- PE = Process element
- PFH = Probability of failure per Hour
- PMHF = Probabilistic metric for random hardware failures
- PrcC = Process characteristic
- PrdC = Product characteristic
- QM = Quality method
- QR = Quality rule
- Req = Requirement
- RMR = Risk Matrix Ranking
- RP = Reaction plan
- SE = Structure element
- SE ErDet = Structure element for error detections
- SE ErResp = Structure element for error responses
- SFF = Safe failure fraction
- SG = Safety Goal
- SIL = Safety integrity level
- SM = Organisational-SE for “safety mechanisms”
- SPF = Single point fault
- SPFM = Single point fault metric
- TF = Top failure of a top function
- TFn = Top function at root element
- TS = Test sample
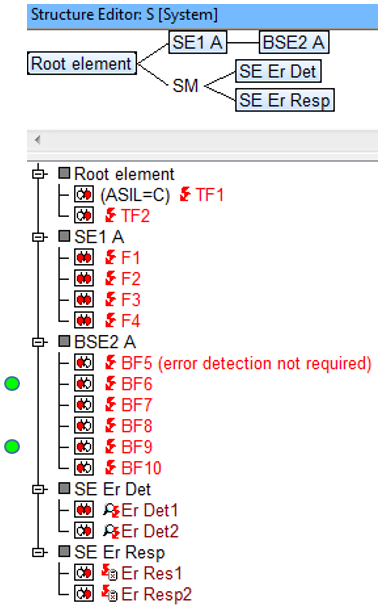
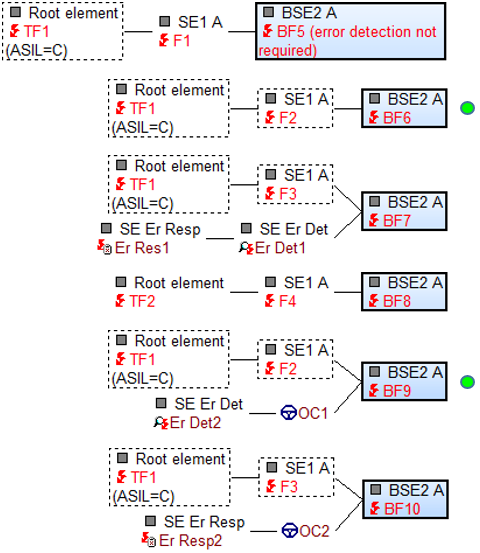
This structure consists of three structure elements to which failures are assigned and two structure elements that have safety mechanisms.
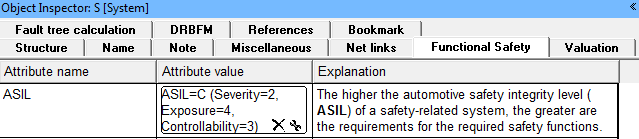
- TF1 is a safety-critical failure. It has been assigned a value of ASIL = C via the tab “Functional Safety” in the Object Inspector.
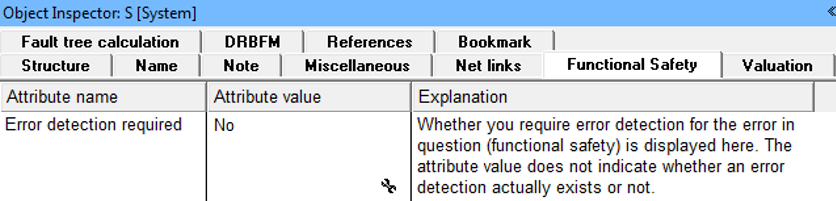
- BF5 is a base failure (BF), which does not need an error detection assigned, although BF5 has a safety-critical failure TF1 as an effect. The decision that no error detection is required is made in the Object Inspector under the “Functional Safety” tab.
- BF6 is a base failure (BF) to which no safety mechanisms (error detection and error response) are assigned, although it has a safety-critical failure TF1 as an effect.
- BF7 is a base failure (BF) which has a safety-critical failure TF1 as an effect and to which safety mechanisms (error detection and error response) are assigned.
- BF8 is a base failure (BF) which has no safety-critical failure as an effect and no safety mechanisms either.
- BF9 is a base failure (BF) which has the safety-critical failure TF1 as an effect. In addition, BF9 is assigned to an operating condition which is followed by error detection.
- Finally, BF10 is a base failure (BF) which has the safety-critical failure TF1 as an effect. BF10 is also assigned to an operating condition, but this is followed by an error response.
The correlations described above are displayed in the Graph Editor and in the Failure Net Editor:
Graph Editor from viewpoint of BF
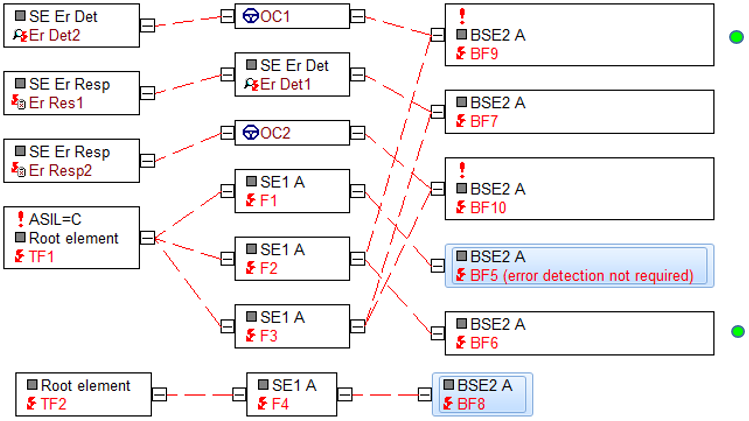
Failure Net Editor from viewpoint of BF
Search result ![]() :
:
BF6 und BF9 werden als Basisfehler ausfindig gemacht, die durch keine Fehlerreaktion abgesichert sind, obwohl beide BF einen sicherheitskritischen Folgefehler aufweisen. Ob zwischen dem BF und der Fehlerreaktion eine Fehlererkennung oder/und ein Betriebszustand angeordnet sind oder nicht, hat für das Suchergebnis keine Bedeutung.
BF6 und BF9 are base failures not protected by an error response, although both BFs have safety-critical failure effects. Whether an operating condition is arranged between the BF and the error response or not is of no significance for the search result.